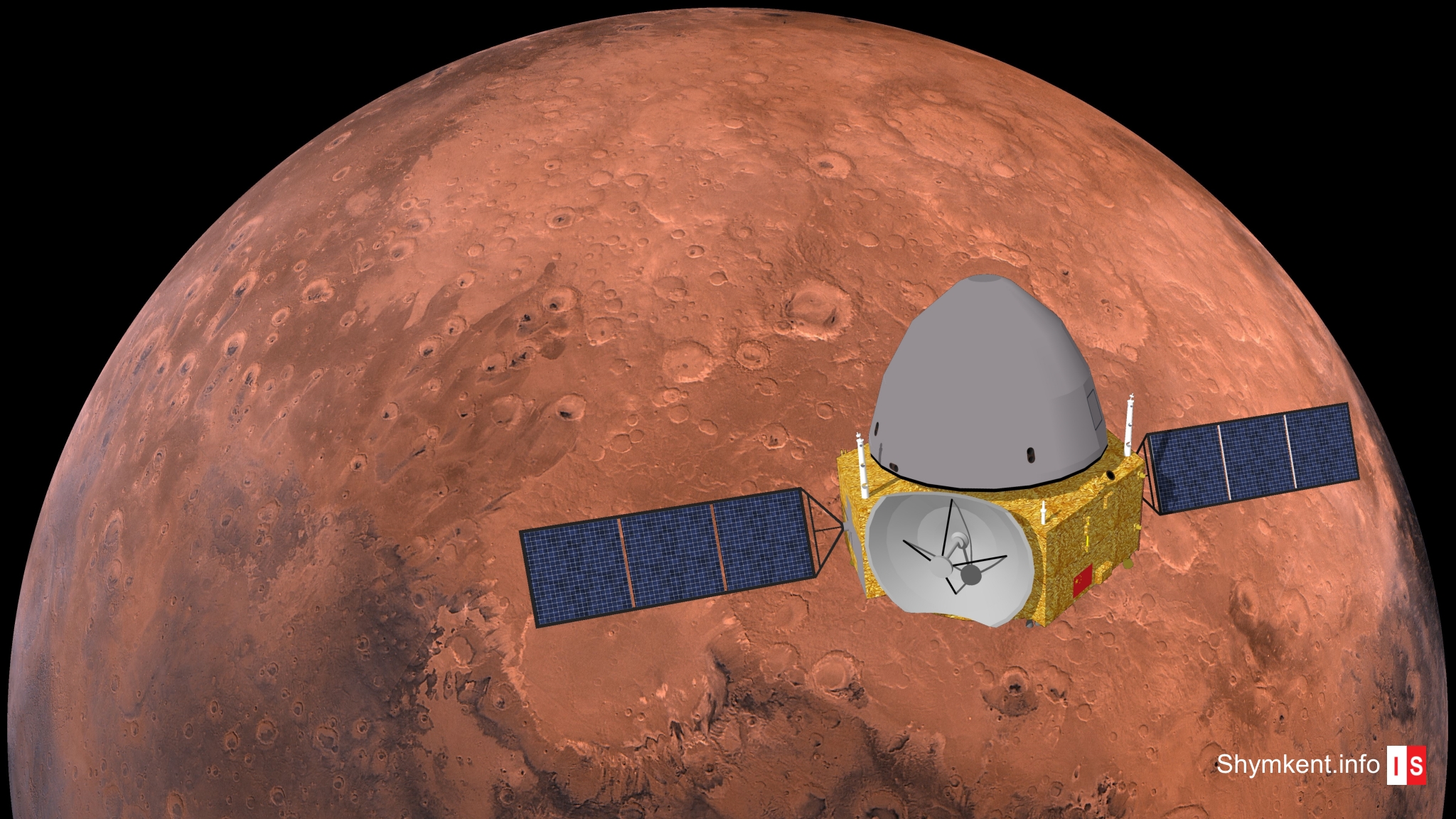
The Mars mission Tianwen-1 is China’s first mission to Mars and it is a ambitious one. They want to reach orbit, landing on the ground and to drive on the mars surface with a rover.
The Tianwen-1 spacecraft is the first flagship mission of China’s planetary science program. Tianwen-1 means Heavenly questions-1 in Chinese language. The spacecraft was launched on China’s strongest rocket Long March 5 at 23th July 2020 at Wenchang Spaceport at Hainan Island in China. During it’s six month flight to Mars the spacecraft made a selfie by deploying a small cubesat – called Tianwen Deployable Camera (TDC) – on 6th October 2020. The cubesat made a photo of the Orbiter and Lander in front of the dark sky of the interplanetary space.
If everything goes well the orbiter will enter the Mars orbit at 12:01pm UTC / 06:01pm Almaty time on 10th February 2021. The Tianwen-1 mission is not only a Orbiter – it’s also a lander and a Mars rover. So this mission is very ambitious for a first try at the Red Planet.
Even the scientific payload is very advanced. The Orbiter has a Mars Magnetometer (MM) to analyze Mars magnetic field, a Subsurface Detection Radar (OSR) to analyze the structure under the Mars ground, a Mars Mineralogy Spectrometer (MMS) to have a look on the geological elements on Red Planets surface. Last but not least the Orbiter is home of two cameras, High-Res Camera (HRC) and Medium Resolution Camera (MRC), to make photos of Mars during its operation time around Mars.
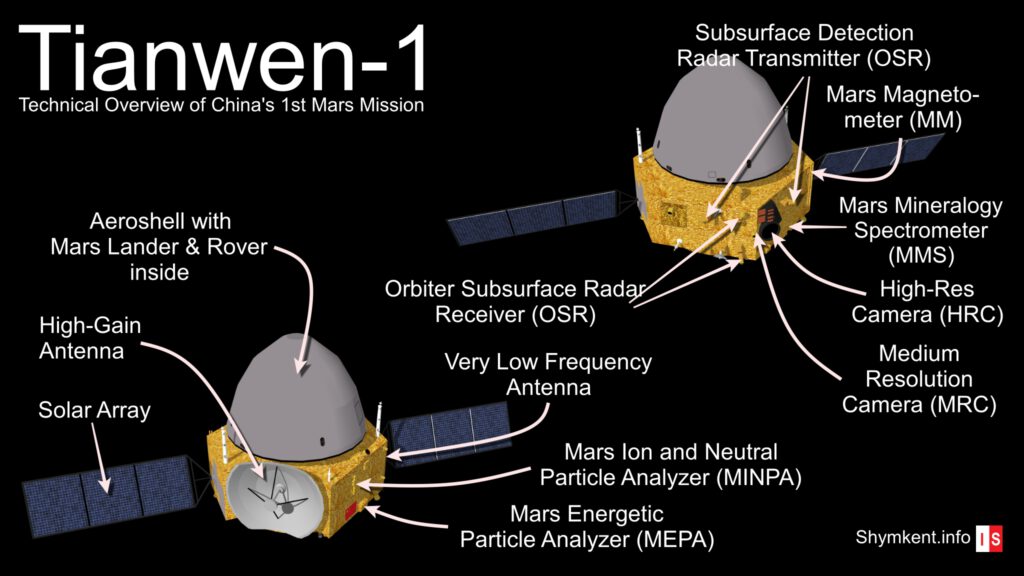
The orbiter of Tianwen-1 with a weight of 3,175 kg – if also everything goes right – will operate around Mars for two earth years.
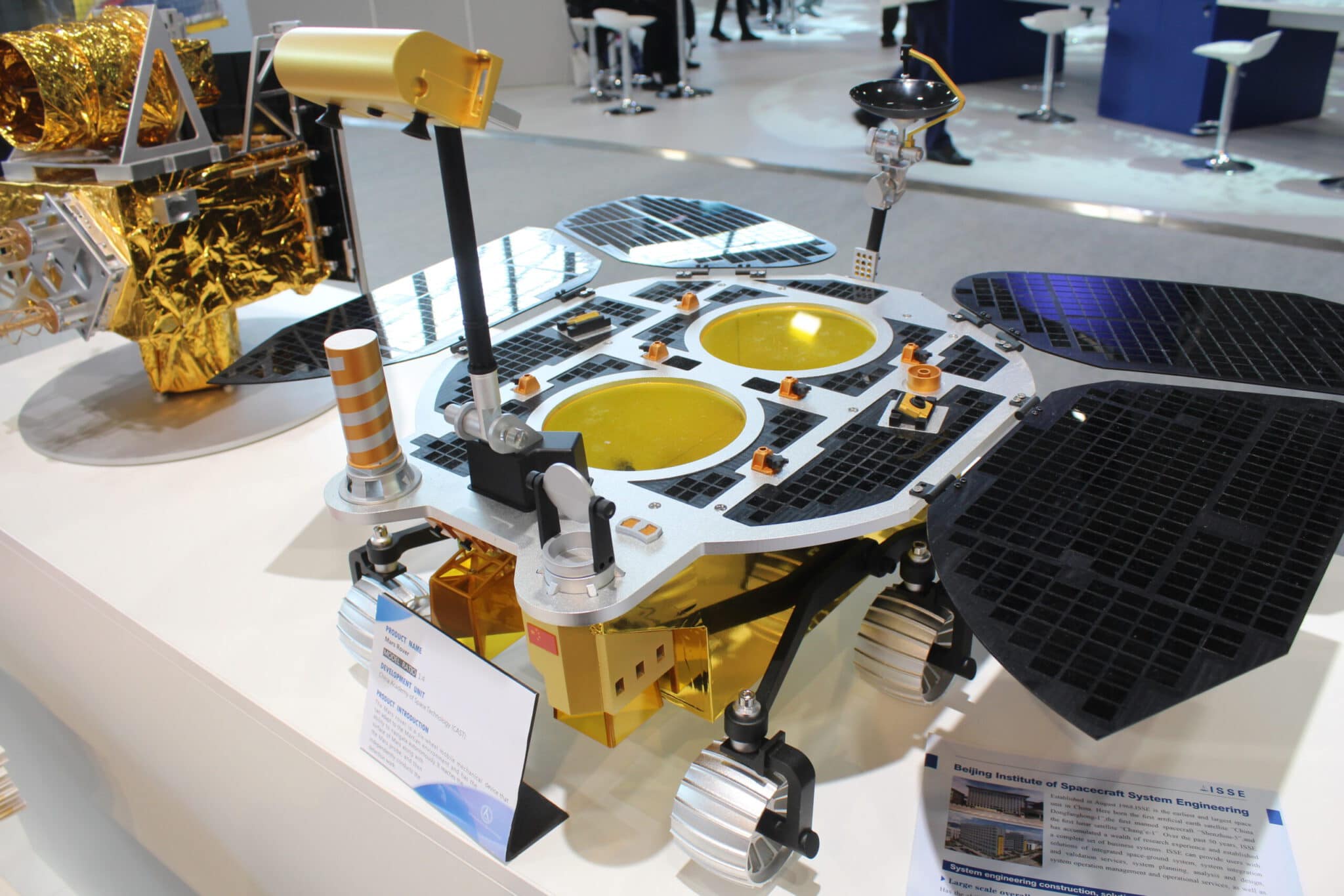
The lander will land in May 2021 on the Mars surface in the Utopia Planitia region. After a soft landing the Mars rover with a weight of 240 kg will leave the lander and will explore the Martian rocks. This will make China to the second nation that will operate a rover on Mars – just after the United States.

You can watch this YouTube video to get a detailed view of the full mission profile of Tianwen-1:
Mission timeline
From draft to launch
November 2015: China revealed that they want to launch a planetary mission to Mars in 2020. The mission will have a Orbiter, a lander which will land by rocket engines and parachute. Onboard of the lander will be a rover. The Mars rover will have a size of NASA’s Mars Exploration Rovers Opportunity and Spirit. The working title is Huoxing-1.
November 2018: China selected two potential landing sites for their rovers. The first candidate is Chryse Planitia and the second candidate is Isidis Planitia.
10th April 2020: The Mars spacecraft arrived at Hainan Island for the last preparations before launch.
24th April 2020: China’s first Mars mission changed it’s name from Huoxing-1 to Tianwen-1 at China’s Cosmonautics Day.
24th May 2020: The Long March 5 rocket needed for this mission arrived at Hainan Island.
23rd July 2020: Tianwen-1 was launched 04:41:15 UTC from Wenchang Spacecraft Launch Site with a Long March 5 rocket.
Tianwen-1’s way to Mars
28th July 2020: Before China’s first Mars mission left the Earth-Moon system it made a picture back to it’s home planet and the Moon. The picture was made 1.2 million kilometers away from our Blue Planet.
2nd August 2020: Tianwen-1 performed it’s first trajectory correction maneuver by ignite the main engine for around 20 seconds.
30th September 2020: Tianwen-1 sent a Selfie back to earth. It deployed a mini satellite with a camera. This satellite made some pictures of the spacecraft and send this picture via Wi-Fi back to Tianwen-1. On this day Tianwen-1 was travelled already 188 million kilometers and was about 24.1 million kilometers away from our planet Earth.
10th October 2020: The second trajectory correction burn was performed by Tianwen-1. The main engine was fired for eight minutes. The spacecraft was 29.4 million kilometers away from Earth.
28th October 2020: Tianwen-1 executed the third trajectory correction maneuver. The spacecraft fired eight 25N engines. It was also a calibration test of this 25 Newton engines. China’s Mars spacecraft was 44 million kilometers away from the earth
5th February 2021: China’s Mars spacecraft sent first picture of Mars back to earth. The picture was made 2.2 million kilometers away from Mars.
Tianwen-1 at Mars
10th February 2021: China’s first planetary science mission to Mars entered the Mars orbit successfully.
15th February 2021: Tianwen-1 performed a major orbit inclination change to switch to a polar orbit around Mars. The polar orbit is important to map the Red Planet.
20th February 2021: The orbiter started to decrease the Mars orbit apogee from 180,000 to 60,000 km. The orbit period is down from 10 days to 2 days for one orbit.
24th February 2021: Tianwen-1 arrived it’s 2-sol reconnaissance orbit (280 x 59,000 kilometres). This orbit will be used to map Mars and to make the final decision for the correct landing zone for the rover in NET May.
4th March 2021: First batch of high-res images in b/w and color was released: one color image with North Pole of Mars and two pan-image from Utopia Planitia.
24th April 2021: The rover of the Tianwen-1 mission got a name: Zhurong (Chinese: 祝融 – the ancient Chinese god of Fire)
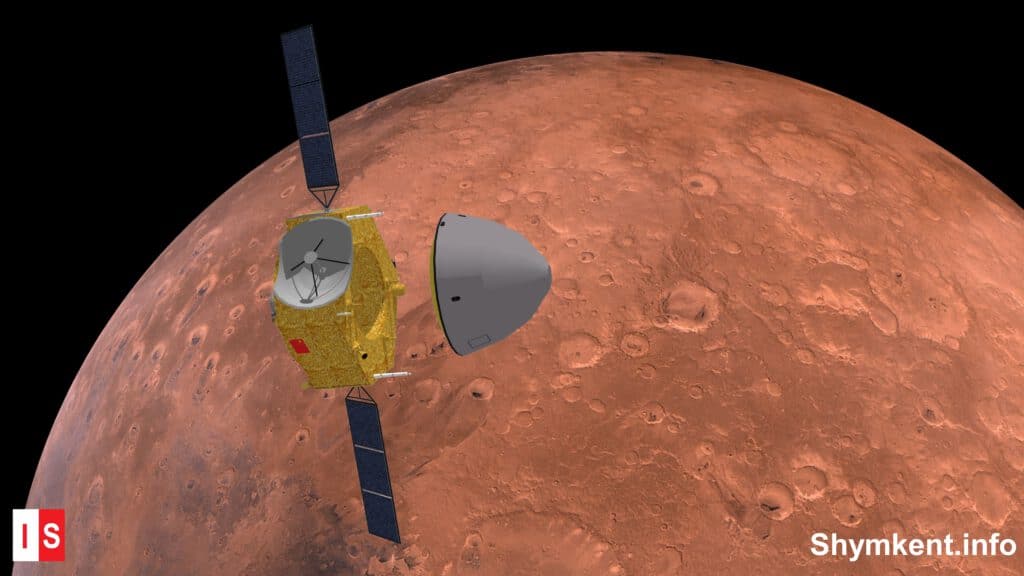
14th April 2021: The landing attempt of the Chinese Mars Rover Zhurong started at around 23 UTC on April 14th. The landing site is in Utopia Planitia at Mars coordinates 24.748°N, 110.318°E. Tianwen-1 made already many high-res images of the landing site to find the best and safest place for the rover.
| Time | Event |
| – 5 hours (~6pm UTC) | 277.000 km above Mars the Tianwen-1 spacecraft will perform the last maneuver by lowering the orbit to about a height of 50 km above the planned landing site. |
| – 5 min (~ 11pm UTC) | Separation of the Lander section from Tianwen-1. The Tianwen-1 spacecraft is performing another maneuver to not dip to much into the martian atmosphere. |
| +/- 0 sec | Landing capsule entering the Mars atmosphere at around 125 km above the Mars surface with a velocity of 4.8 km/s. |
| + 1 min 40 sec | Maximum heat on the heat shield of the lander at around 40 km above Mars. |
| + 4 min 44 sec | Parachute deploy at around 10 km above martian surface. The lander has a speed of 460 m/s. |
| + 5 min 10 sec | Heat shield separation. The lander is flying with a speed of 250 m/s to the ground. Lander radar and camera is searching to detect the area of the final landing site. |
| + 6 min 10 sec | Separation between lander and parachute at around 1000 meters above the surface. The lander is starting to fire its landing engines and is flying to the target landing zone. |
| + 6 min 50 sec | The lander reduced with the landing engines its speed close to zero and is performing now the last landing correction to land on the correct landing site. |
| + 7 min 30 sec | The legs recognize contact with the ground. The landing engines stop working. Landing completed in Utopia Planitia. |
15th April 2021: Chinese Mars Rover Zhurong made a successful touchdown in Utopia Planitia at 25.1°N, 109.7°E at 23:18 UTC on 14th April. The confirmation of the landing was released in China’s News Channels at 12:45 UTC on 15th April.
The Tianwen-1 orbiter started immediately to change its science orbit into an relay orbit to overpass the landing site of Zhurong three times a day. The reconfiguration of the orbit needs around three days. During this time it is not possible to receive images from Mars rover Zhurong because the Tianwen-1 orbiter is required as a relay for the Mars – Earth data link to transport larger data sets like images or scientific data. That means not that China’s CNSA has not a contact to their rover in this time. They have a direct – but low data link between 16kbps (normal) and 32 bps (emergency) between rover and Earth.
17th May 2021: The Tianwen-1 orbiter reached its relay orbit with a period of 8.2 hours. In the future – during a surpass of Tianwen-1 orbiter over the landing site a high-data communication of 20 Mbit (UHF) up to 50 Mbit (X-Band) will be possible.
19th May 2021: First images of Mars rover Zhurong was received on 19th May 2021 at 1am UTC (Sol 4). The showed one picture of the navigation camera (Black&White) and a view of the already deployed ramp down to the martian surface. The other was a picture from the Panoramic Camera (Color) of Zhurong which was a selfie with the deployed solar arrays, the high-gain antenna and the surrounding martian surface in focus..
22nd May 2021: China’s Mars rover Zhurong rolled down from the descent module to the martian ground (Sol 7).
28th May 2021: Science program started on the surface on 28th of May (Sol 14). Zhurong will perform 90 days of science on the Mars. After 90 days CSNA will slow down or stop the mission of the Mars rover. The Tianwen-1 orbiter will change it’s orbit again. The orbiter will enter a science & mapping orbit to inspect and to map the planet Mars.
11th June 2021: China likes selfies. Like the photo sessions of Yutu-1&2 with the Chang’e-3&4 landers on the Moon also Zhurong performed a photo session with the rover and the descent module. The rover Zhurong made the photo by deploying a small camera on the ground and driving back near the descent module. Later, on 26th June, also a video was published showing the rover driving over the martian surface filmed by the small camera.
8th July: The rover is still driving south and passed the 300-meter-mark. It’s next destination is the parachute and back-shell of the lander still around 130 meters away.
15th July: The Chinese rover reached the parachute and back-shell of the lander and made some photos of them. These items went down around 350 meters away from the landing site. Zhurong has been working for 60 Sols and has traveled 450 meters on the martian surface so far.
6th August: On Sol 82 Mars rover Zhurong had driven 808 meters. Also orbiter Tianwen-1 has sent back to Earth over 180 GB of scientific raw data.
15th August 15: A huge milestone is reached. The Zhurong rover has completed its primary mission and operated for 90 martian sols or about 92 earth days on the martian surface. It drove over 889 meters and all scientific payloads are still working well. Over 10GB of raw data was sent via Tianwen-1 orbiter back to earth.
23rd August 2021: Zhurong rover achieved a total drive of one kilometer at its 100th day on the Martian surface.
30th August 2021: The Chinese Mars rover traveled 1064 metres so far and provided another high-res panorama image of the current location near a sand dune.
13th September 2021: Tianwen-1 and Zhurong went into a planned save mode. The reason is the solar conjunction between Earth and Mars. It means the Sun is between Earth and Mars and blocks the direct communication between Earth and the spacecrafts at Mars.
25th October 2021: Zhurong sent back a first signal after the planned lost communication during the month long solar conjunction.
7th November 2021: ESA started with CNSA the first of five communication tests between Mars Express and Zhurong. The test will try to download data from Zhurong and will send the data via Mars Express back to Earth. The next communication test were planned for 16th, 18th, 20th and 22nd November 2021.
9th November 2021: The orbiter Tianwen-1 went from the Relais orbit for Zhurong into its final Science Orbit. The four 102N engines worked for 260 seconds. The new orbit is a 260×10,000km strong elliptical orbit.
15th May 2022: The Mars rover Zhurong achieved his first earth year on Mars. The Chinese planetary rover drove 1,921 m on the martian surface.
18th May 2022: The martian winter is coming. The rover started hibernation to save power. The highest temperature at Utopia Planitia is already -20°C during the day and goes down to -100°C at night. If everything goes well Zhurong will wake up around December when it’ll be spring on Mars. On the same day the Chinese CNSA released another batch of satellite images of Mars made by orbiter Tianwen-1.
Long distance goal: It is planned that Zhurong will drive to destination currently around 10 kilometers away. The destination are interesting mud volcanoes on the martian surface.